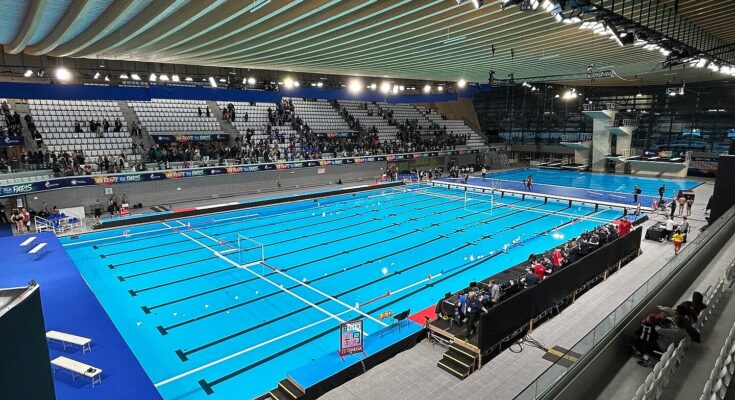
The growing use of artificial intelligence (AI) is creating a greater demand for data centers. These AI data centers generate a lot of heat, but one of these is putting that heat to good use for the Paris Summer Olympics swimming pool.
A US company, Equinix, owns a data center that produces extra heat from its many servers. According to FOX Business, instead of allowing the heat to be wasted, the company is channeling it to warm the swimming pool at the nearby Paris Olympics Aquatics Centre, ensuring it’s comfortably warm for athletes.
AI data centers use immense amounts of energy to run large groups of servers. These servers work with data to train AI programs, such as ChatGPT. Keeping these servers cool is important because they can get quite hot, often even getting hotter than 80 degrees Fahrenheit. To cool them down, fans and liquid cooling systems are commonly used.
One such data center, known as PA10, was opened by Equinix in 2023 at their campus in Saint-Denis, France. This center is built to handle powerful server setups that train AI models. It also uses special technology to export excess heat generated by the servers.
Providing heat to Olympic Aquatics Centre and 600 homes
Equinix informed Wired that they anticipate exporting 6.6 thermal megawatts of heat from their data center when it’s fully operational. This amount of heat could help keep more than a thousand homes warm.
A data center owned by @Equinix is capturing and reusing heat produced by servers to funnel heat that helps keep the swimming pool at Paris @Olympics Aquatics Centre. As an energy source it will spare the region 1,800 metric tons of CO2 emissions per year. @Paris2024 pic.twitter.com/CbfgTOLLji
— Pick Up Project
(@Pick_Up_Project) August 10, 2024
To help heat the pool at the Olympic Aquatics Centre, Equinix partnered with a French utility company, Engie. They redirected the excess heat from the data center into Engie’s energy system through pipes.
The heat is then used to warm the aquatics center’s pool, as well as heat about 600 nearby homes and local businesses, according to FOX Business.
Growing plants using the heat in the greenhouse
The new setup benefits Equinix, as well, allowing the company to utilize less energy for its cooling system by exporting excess heat. Additionally, Equinix has established a rooftop greenhouse on top of the data center. In this greenhouse, strawberries, tomatoes, and other plants are grown, using the heat that’s redirected from the facility.
Noah Nkonge, who leads the heat export efforts at Equinix, shared on the company’s website that the PA10 data center in Paris will provide surplus heat at no cost for 15 years. Moreover, the heat will be transferred to the Plaine Saulnier urban development zone. This includes the surrounding neighborhood and the Olympic pool.
Equinix has a long history with heat exporting technology. In 2010, the company launched the world’s first heat export project at a facility in Helsinki, where the excess heat is used to warm nearby homes.