The largest dinosaurs ever lived during the Mesozoic Era, and the Titanosaurs were one such group of sauropods. They roamed the Earth in the last part of the Cretaceous Period, and their fossils have been discovered all over the world.
Unfortunately, these giant dinosaurs, five of which are closely looked at below, disappeared at the end of the period.
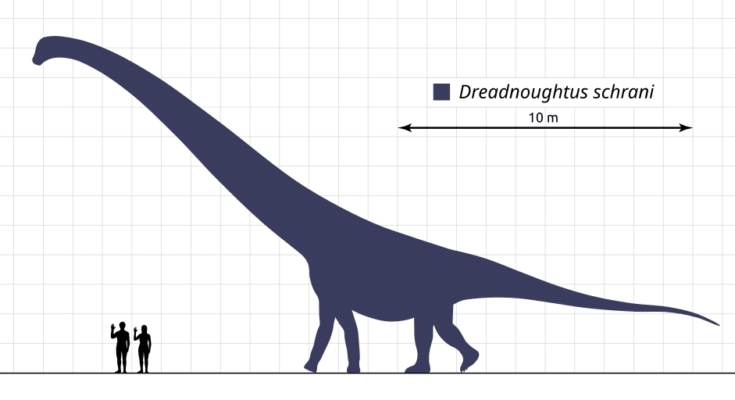
Dreadnoughtus
The Dreadnoughtus was one of the largest titanosaurs, and some researchers believe it may have even been the biggest. This dinosaur measured about 26 meters long (85 feet) and weighed an estimated 59 metric tons.
Its fossils were found in southern Patagonia, Argentina, from rocks that date back to about 77 million years ago. So far, only one such species has been discovered, known as D. schrani.
Patagotitan mayorum

Patagotitan mayorum is considered one of the largest land animals to have ever existed. This dinosaur was discovered through a large collection of fossilized bones, including a massive thighbone that was 2.4 meters long (roughly 8 ft). Before it was formally named in 2017, it was often simply referred to as “the Titanosaur” due to its enormous size.
Researchers estimate it may have weighed around 70 metric tons and stretched up to 37.2 meters (122 feet) in length, though some experts believe these measurements might be too high. Patagotitan lived between 100 and 95 million years ago.
Argentinosaurus
Argentinosaurus lived on the then-island continent of South America somewhere between 97 and 93.5 million years ago, during the Late Cretaceous Period.
It is among the largest known dinosaurs and this is the size of its leg (human for scale). pic.twitter.com/BwyXtjMmEy
— Massimo (@Rainmaker1973) August 5, 2024
The Argentinosaurus has been known to scientists since 1993, though its fossils were first discovered in 1987 on a ranch in Argentina. The rancher who found the fossil initially thought it was a large piece of petrified wood, but later it was identified as a vertebra from a new species of giant sauropod.
Although no full skeleton has been found, researchers have estimated its size based on the fossils that do exist. Argentinosaurus is believed to have measured between 37 and 40 meters long (about 121 to 131 feet) and may have weighed between 90 and 100 metric tons.
Saltasaurus
Today’s #Dinosaur of the Day is Saltasaurus!
70-68 million years ago #Cretaceous
Upto 28ft long, 3 tonnes
South America pic.twitter.com/yQaOjn8B0d
— Dino Tweets
(@Dino_Tweeter) March 13, 2024
Saltasaurus, a titanosaur named after the city of Salta in northern Argentina, was first described in 1980. Unlike other titanosaurs, it was relatively small, measuring about 12.2 to 12.8 meters long (40 to 42 feet) and weighing just under 7 metric tons.
While many larger titanosaurs relied on their size to protect themselves from predators, Saltasaurus had a different defense. Fossil evidence suggests its body was covered with bony plates, called osteoderms, which acted like armor to protect it from attacks by making it harder for predators to bite through its skin.
Rapetosaurus krausei
Daily Dino
; Rapetosaurus krausei
A 15meter titanosaur sauropod from Maastrichtian Madagascar, Rapetosaurus is known from fairly complete juvenile specimens and fragmentary adults. It showed that Titanosaurs are more closely related to Brachiosaurids than to Diplodocids pic.twitter.com/deJZ4WOP6l
—
Dino Kia
Atreides Chaos Theorist
(@YutyTyrant) May 25, 2023
In 1998, researchers in northern Madagascar discovered the skeleton of a juvenile Rapetosaurus krausei during excavations on a hillside. This find was significant because it was one of the most intact titanosaur skeletons ever uncovered.
Along with the juvenile skeleton, they also found skulls from both a juvenile and an adult. The juvenile skeleton was about 8 meters long (26 feet), but scientists believe that adults of this species could grow up to 15 meters (49 feet).
The fossils of Rapetosaurus date back to around 70 million years ago just 4 million years before the K-T extinction, one of the largest mass extinction events in Earth’s history.