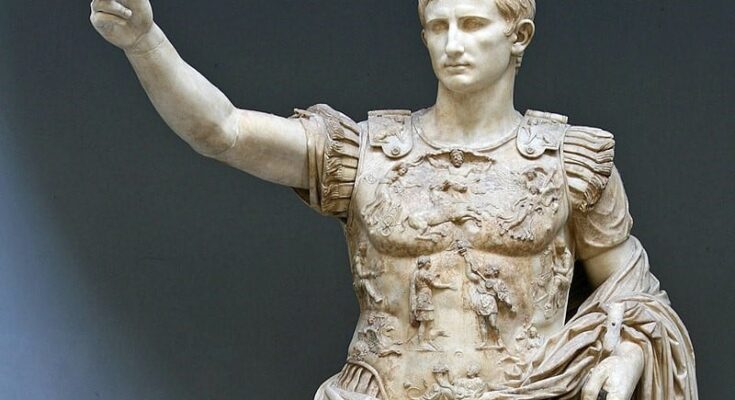
Roman law has had a profound and enduring influence on the development of legal systems worldwide, including that of the United States.
While the US legal system is primarily based on common law traditions inherited from England, the principles and structures of Roman law have significantly shaped its foundations.
Roman law was one of the most sophisticated legal systems of the ancient world. Its principles laid the groundwork for many legal fundamentals still in use today in the West. It formed the basic framework for civil law. Its development spanned over a millennium, with several key components defining its structure.
The development of Roman law
The Twelve Tables completed in 449 BC were the earliest attempt at creating a code of law for Rome. It was a consolidation of earlier traditions, stating the rights and duties of a Roman citizen. These laws were publicly displayed and covered various aspects of daily life, including property, family, and civil procedure. The codification was significant in ensuring transparency and fairness in the Roman legal system.
The Praetor, a judicial magistrate, had the authority to issue edicts (The Praetorian Edicts) every year to complement and adapt existing laws. These edicts allowed for flexibility and responsiveness to new legal challenges, thereby ensuring the relevance and adaptability of Roman law.
The Corpus Juris Civilis (Body of Civil Law) was commissioned by Emperor Justinian and compiled in 529 to 534 AD. The Corpus Juris Civilis was a comprehensive codification of existing Roman laws and legal commentary. It consisted of four main parts. The first was the Codex Justinianus, which compiled all of the extant imperial constitutions from the time of Hadrian. The second part, the Digest (Digesta) or Pandects (Pandectae), was issued in 533.
It compiled the writings of great Roman jurists such as Ulpian along with current edicts. The third part, the Institutes (Institutiones), was intended as a sort of legal textbook for law schools. Later, Justinian issued a number of other laws, mostly in Greek, which were called Novels (Novellae). This compilation served as a cornerstone for the preservation and transmission of Roman legal principles.
Legal scholars were an important part in the development of Roman law. Roman legal thought was profoundly influenced by legal scholars, known as jurists, who provided interpretations and opinions on legal matters. Their writings and commentaries helped shape Roman jurisprudence and ensured the coherence and development of the legal system.
Fundamental principles and concepts
Several fundamental principles and concepts that we take for granted today originated in ancient Rome. These principles and concepts have had a lasting impact on modern legal systems. Concepts such as citizen rights and obligations within society, legal relationships between citizens, and obligations to the state—or the state’s obligation to its citizens—as well as family law stem from Rome. The focus on legal relationships and the duties of citizens formed the basis for many modern legal doctrines.
The concept of a legal person, whereby entities such as individuals, corporations, and states are recognized as having legal rights and obligations, originated in Roman law. Sophisticated rules regarding the ownership, transfer, and use of property are principles which continue to underpin property law in many contemporary legal systems.
Roman law also established the principle of the contract. This would include the formation and enforcement of contracts, such as mutual consent, consideration, and obligations of the parties involved. Finally, the procedural aspect of modern legal systems such as the role of the judge, the rights of litigants, have influenced the development of modern judicial procedures.
Transmission of Roman law
The fall of the Western Roman Empire did not mark the end of Roman law. It was preserved and adapted by various medieval European states. During the 11th and 12th centuries, the rediscovery of the Corpus Juris Civilis in Italy led to a revival of Roman legal studies. The establishment of universities, particularly the University of Bologna, played a crucial role in disseminating Roman legal principles throughout Europe.
During the Renaissance, scholars revisited classical Roman texts, leading to renewed interest in Roman law. The principles of Roman law were integrated into the legal systems of many European countries. During the Enlightenment, legal thinkers such as Montesquieu and Blackstone further propagated Roman legal concepts, which influenced the development of modern legal systems.
The most important impact of Roman law was its influence on civil law systems, serving as the foundation in several countries in Continental Europe, Latin America, and parts of Asia and Africa. These systems are characterized by comprehensive codifications of laws, similar to the Corpus Juris Civilis.
Influence on US legislation
The Founding Fathers of the United States were well-versed in Classical education, which included the study of Roman law. Figures such as Thomas Jefferson, John Adams, and James Madison drew upon Roman legal principles when framing the US Constitution and other foundational documents. For instance, the concept of a mixed government with checks and balances reflects the Roman idea of a balanced constitution.
Other concepts in the US Constitution that derived from the Romans are the separation of powers, vetoes, filibusters, quorum requirements, term limits, impeachments, the power of the purse, and regularly scheduled elections.
US common law is influenced by Roman law in several ways. This can be seen in the principles of property rights and ownership as well as the transfer of such rights. Easements and servitudes are likewise derivative. In addition, principles of contract law, including mutual consent, consideration, and the binding nature of agreements are rooted in Roman legal doctrines.
Furthermore, Roman law’s treatment of personal injury and liability has influenced the development of tort law in the United States. The principles of fault, negligence, and compensation have clear parallels in Roman legal thought.
In regards to civil procedure, such as the roles of judges, the rights of litigants, and the structure of legal proceedings, Roman law principles have informed the development of civil procedure in the US legal system.
Finally, Roman law continues to be a part of legal education in the United States. Many law schools include courses on Roman law and its influence on modern legal systems, ensuring that future lawyers understand the historical foundations of contemporary legal principles.